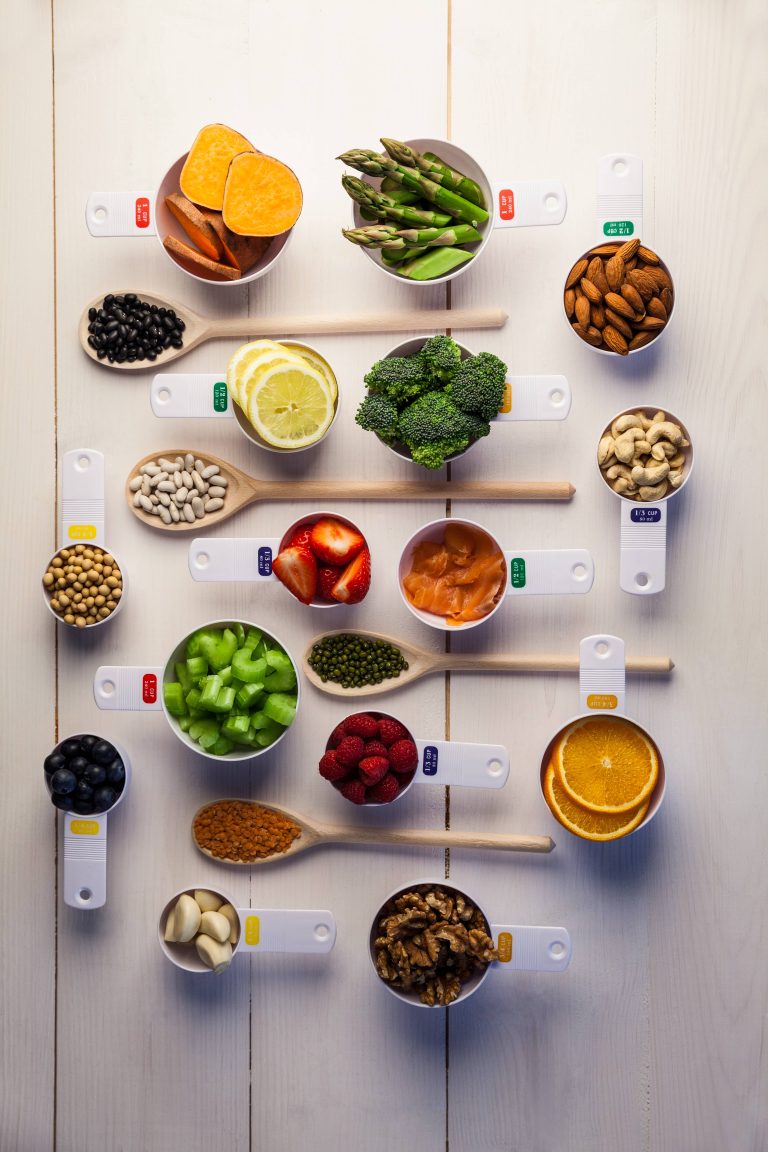
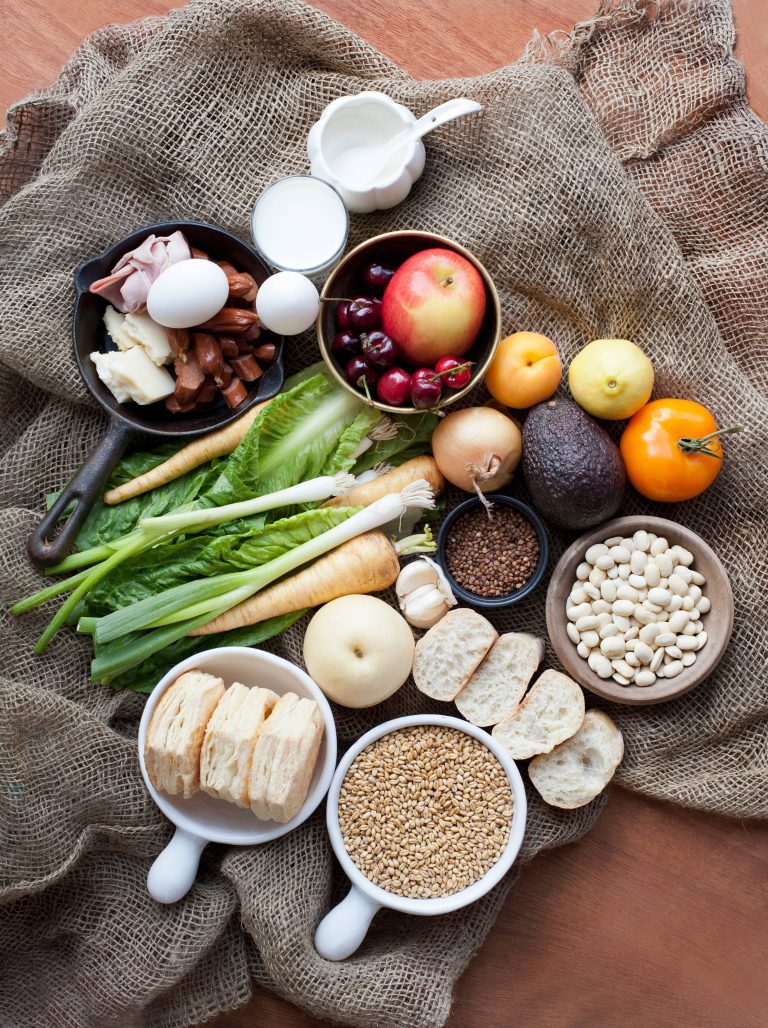
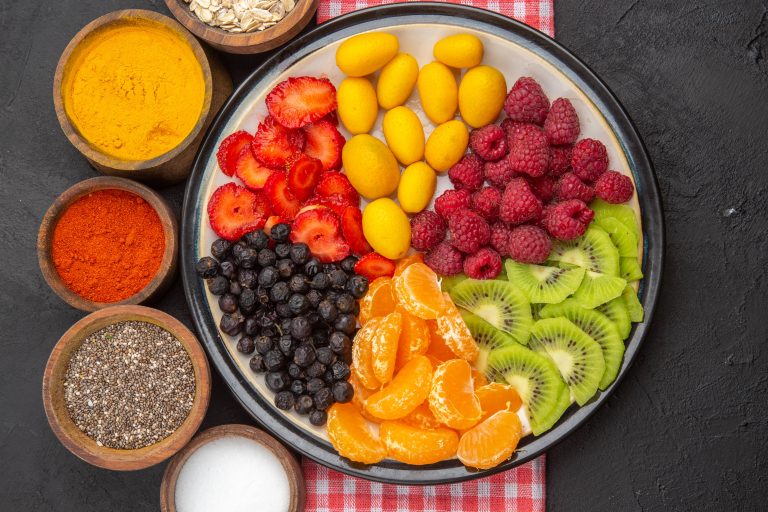
In the world of nutrition, fiber often takes a backseat to more glamorous nutrients like protein and omega-3 fatty acids. However, this unsung hero plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. A fiber-fueled diet can offer a myriad of benefits, from improving digestive health to reducing the risk of chronic diseases. In this blog post, we will explore the various advantages of incorporating more fiber into your diet and provide practical tips on how to do so.
What is Dietary Fiber?
Dietary fiber, also known as roughage, is the indigestible part of plant foods. Unlike other nutrients, fiber is not absorbed by the body. Instead, it passes relatively intact through the stomach, small intestine, and colon, eventually being excreted. There are two main types of dietary fiber: soluble and insoluble.
– Soluble Fiber: This type of fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance. It can help lower blood cholesterol and glucose levels. Soluble fiber is found in foods like oats, peas, beans, apples, citrus fruits, carrots, and barley.
– Insoluble Fiber: This type of fiber promotes the movement of material through your digestive system and increases stool bulk, which can be beneficial for those who struggle with constipation or irregular stools. Whole-wheat flour, wheat bran, nuts, beans, and vegetables like cauliflower, green beans, and potatoes are good sources of insoluble fiber.
The Health Benefits of a Fiber-Fueled Diet
1. Improved Digestive Health
One of the most well-known benefits of fiber is its ability to promote healthy digestion. Insoluble fiber adds bulk to the stool and helps food pass more quickly through the stomach and intestines, which can prevent constipation. Soluble fiber, on the other hand, can help manage diarrhea by absorbing excess water in the intestines.
2. Weight Management
Fiber-rich foods tend to be more filling than low-fiber foods, which can help you feel full longer and reduce overall calorie intake. This is particularly beneficial for those looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight. High-fiber foods also tend to take longer to eat and are less “energy dense,” meaning they have fewer calories for the same volume of food.
3. Blood Sugar Control
For individuals with diabetes, fiber—particularly soluble fiber—can slow the absorption of sugar and help improve blood sugar levels. A diet high in fiber can also reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
4. Lower Cholesterol Levels
Soluble fiber can help lower total blood cholesterol levels by lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL), or “bad” cholesterol levels. Studies have also shown that high-fiber foods may have other heart-health benefits, such as reducing blood pressure and inflammation.
5. Reduced Risk of Certain Cancers
Some research suggests that a high-fiber diet is linked to a reduced risk of colorectal cancer. Fiber’s role in promoting regular bowel movements and removing waste from the body quickly may help prevent the development of cancerous cells in the colon.
6. Heart Health
A diet rich in fiber can improve heart health by reducing blood pressure, inflammation, and cholesterol levels. This, in turn, can lower the risk of heart disease.
How to Incorporate More Fiber into Your Diet
1. Start Your Day with Whole Grains
Choose whole-grain cereals or oatmeal for breakfast. Look for cereals with at least 5 grams of fiber per serving. You can also add fruits like berries or bananas to increase the fiber content.
2. Snack on Fruits and Vegetables
Keep fresh fruits and vegetables handy for snacks. Apples, bananas, carrots, and celery sticks are great options. Dried fruits like apricots, figs, and prunes are also high in fiber.
3. Add Legumes to Your Meals
Incorporate beans, lentils, and peas into your meals. They are excellent sources of fiber and can be added to soups, stews, salads, and casseroles.
4. Choose Whole Grains
Opt for whole-grain bread, pasta, and rice instead of their refined counterparts. Whole grains retain more fiber and nutrients.
5. Include Nuts and Seeds
Sprinkle nuts and seeds on salads, yogurt, or oatmeal. Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are particularly high in fiber.
6. Read Food Labels
When shopping, check the nutrition labels for fiber content. Aim for products with higher fiber content per serving.
Conclusion
Incorporating more fiber into your diet is a simple yet effective way to improve your overall health. From enhancing digestive health to reducing the risk of chronic diseases, the benefits of a fiber-fueled diet are numerous. By making small changes to your eating habits, such as choosing whole grains, snacking on fruits and vegetables, and adding legumes to your meals, you can easily increase your fiber intake and enjoy the many health benefits it offers. Remember, it’s important to increase fiber in your diet gradually to prevent digestive discomfort, and always drink plenty of water to help fiber do its job effectively. Embrace the power of fiber and unlock a healthier, more vibrant you!